Description
Apricot, Prunus armeniaca is a deciduous tree in the family Rosaceae grown for its edible fruit. The apricot tree has an erect growth habit and a spreading canopy. The leaves of the tree are ovate with a rounded base, pointed tip and serrated margin. The tree produces white to pink flowers, singly or in pairs, and a fleshy yellow to orange fruit. The apricot fruit is a drupe that appears similar to a peach with skin that can be smooth or covered in tiny hairs depending on the variety and a single seed enclosed within a protective outer shell (stone).
Apricot trees can reach 8–12 m (26–39 ft) and can live anywhere between 20 and 40 years depending on variety and growth conditions. Apricots may have as many as three centers of origin in China, Central Asia and the Near East with Turkey being the largest producer worldwide. In Africa, apricots are largely grown in South Africa.
Crop Details
Scientific Name: Prunus armeniaca
Common Name: Armenian plum (En)

Apricot blossoms

Ripening fruits

Green fruit on tre

Apricot fruit on tree
Uses & Benefits
Apricots are low in fat but rich in vitamin A and beta-carotene. These nutrients act as antioxidants to protect your cells from damage.
Flavonoids, the antioxidant present in apricots, helps to protect against inflammation and inflammatory illnesses, along with reducing obesity, diabetes, and heart disease risk.
Apricots can be consumed fresh or dried. They may also be processed into jams and jellies, syrup or juice.
Apricot Varieties
Choose varieties suited to local climates and soil conditions. Below are some of the common varieties grown widely.
Moorpark: Known for their sweet and rich flavor. They have a deep orange color and are often considered one of the best-tasting apricots.
Harglow: They are medium-sized, with a sweet and juicy flesh. They are a popular choice for fresh consumption and canning.
Tilton: These apricots are known for their intense apricot flavor. They are good for eating fresh and for making jams and preserves.
Goldrich: Apricots are medium to large in size and have a smooth, sweet taste. They are often used for drying or making apricot-based products.
Blenheim: Blenheim apricots are small to medium-sized and are known for their exceptional flavor. They are often used for making apricot preserves and are sometimes called "Royal" apricots.
Royal Rosa: The apricots have a sweet and slightly tart flavor. They are medium-sized with a pinkish blush on the skin.
Propagation
Basic Requirements
Apricots have a high genetic variability and as a result, they also have a wide range of growing conditions. The trees tend to bloom early compared with other stone fruits and are therefore susceptible to damage from late frosts. Apricots have a chilling requirement (period of cold required to break dormancy) of between 250 and 1200 hours below 7°C (45°F) depending on the variety. Dry climate is good for fruit maturation.
Apricots will grow best in deep, well-draining soils rich in organic matter with a pH of 6 - 7 and will not tolerate water saturating.The Apricot tree will struggle if your soil is shallow, poor, or too heavy, to prevent this amend your soil with well-rotted organic material.
Trees should be watered regularly during the growing season to aid with fruit development. During dry periods, water trees every 10 to 14 days. Apply water deeply and widely, to at least the width of the canopy. Water at ground level to prevent diseases. Add mulch about 3 to 4 inches deep to conserve more water.
Growing from Seed
Apricot trees are usually propagated vegetatively to maintain the desirable genetic characteristic of the parent. Trees can be propagated from cuttings or by budding and grafting.
Cuttings are lengths of stem ranging from 6-9 inches usually taken from the previous year's growth of an established tree. Cuttings are taken in late winter or early spring and rooted so that they produce a whole new tree. When selecting cuttings, choose a branch with three or four leaf buds and cut it at a 45-degree angle. Strip any leaves from the bottom half of the cutting, but leave the leaves on the top half. Keep the new cuttings moist so they stay healthy and strong until you can get them in the ground.
Budding and grafting involves joining two genetically distinct plants; one is used for the lower part called the rootstock and another is used for the upper part, known as the scion. The scion is attached by inserting a bud from the desired variety under the bark of the rootstock so that it produces a new tree. The selection of the rootstock variety is very important since it will affect the tree size, the resistance to soil-borne pathogens, and the drought and frost tolerance of the grafted tree.
Apricot trees should be planted in full sun. In colder regions it is beneficial to plant them close to a north facing wall which helps reduce the speed with which the trees warm in the spring, delaying bloom. Plant bare root trees in a pre-dug hole which is slightly wider than the root ball. Backfill the hole so that the tree is planted to its original planting depth. It is usually possible to identify this from changes in the color of the bark. If planting multiple trees, space them at least 7.6 m (25 ft) apart.
General Care and Maintenance
Apricots should be pruned annually and are generally trained to an open center. Annual pruning encourages new fruit spurs. When pruning begin by removing any dying, dead, or diseased branches, as well as any new branches that are growing inwards to allow sun and air to reach all parts of the tree. Cut back leading branches to stimulate outwards growth and remove any branches that are crossing over or rubbing against each other, as well as any suckers and watersprouts.
When the tree is bearing fruit, it is important to thin the fruits to leave 3 or 4 per cluster. This allows fruits to become larger and prevents the tree from reducing production the following year.
Trees will also benefit from the application of a nitrogen fertilizer in Spring. Phosphorus is essential when the tree starts producing fruits to help in boosting fruit production.
Harvesting
Apricots are ready for harvest when the fruits change from green to yellowish orange in color and feel slightly softened, but still firm to the touch. Pluck ripe fruits by cupping them in your hand and gently twisting to detach it from the stalk.
Store harvested fruits in a cool area free from damaging factors. The fruit is best stored in a single layer to minimize bruising which can lead to decay.
References
CABI Crop Protection Compendium. (2013). Prunus armeniaca datasheet. Available at: http://www.cabi.org/cpc/datasheet/44249. [Accessed 05 November 14]. Paid subscription required.
Lamb, R. C. & Stiles, W. C. (1983). Apricots for New York State. New York's Food and Life Sciences Bulletin No. 100. New York State Agricultural Experiment Station. Available at: http://ecommons.library.cornell.edu/bitstream/1813/5108/1/FLS-100.pdf. [Accessed 05 November 14]. Free to access.
Ogawa, J. M., Zehr, E. I., Bird, G. W., Ritchie, D. F., Uriu, K. & Uyemoto, J. K. (Eds) (1995). Compendium of Stone Fruit Diseases. American Phytopathological Society Press. Available at: http://www.apsnet.org/apsstore/shopapspress/Pages/41744.aspx. Available for purchase from APS Press.
Roper, T., Mahr, D. & McManus, P. (1998). Growing Apricots, Cherries and Peaches in Wisconsin. University of Wisconsin-Extension, Cooperative Extension. Available at: http://learningstore.uwex.edu/assets/pdfs/A3639.PDF. [Accessed 05 November 14]. Free to access.
Common Pests and Diseases
Diseases
Category : Fungal
Armillaria root rot
Armillaria mellea

Armillaria fruiting Bodies

Armillaria mycelial mat
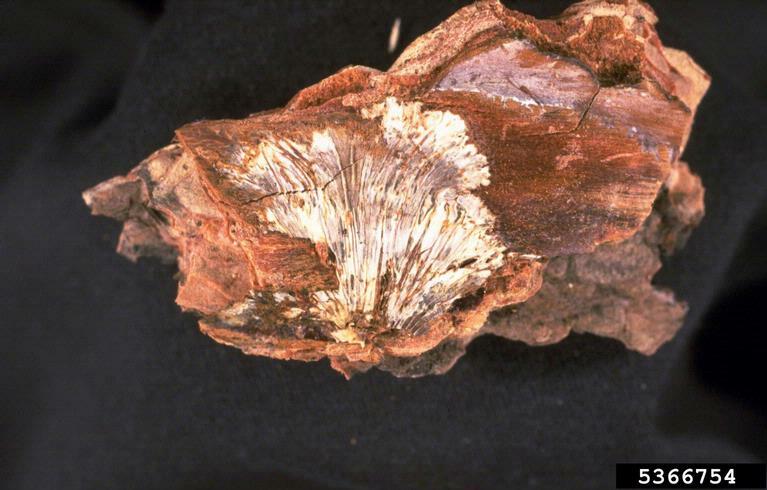

Mushroom and mycelial fan characteristic of armillaria root rot (Armillaria sp.)
Symptoms
If tree is infected after it has reached 5 years of age then typical symptoms include poor terminal growth and small leaves; around midsummer the whole tree suddenly collapses; in orchards trees usually die in a circular pattern; infected trees often have a fan-shaped white fungal mat growing between the bark and wood of the crown.
Cause
Fungus
Comments
Management
Once a tree is infected there is no treatment and it should be removed, fumigants do not control fungi in soil adequately; do not plant apricot in newly cleared forest or on the site of old orchards with a history of Armillaria.
Brown rot blossom
Monolinia spp.

Lesions on apricot fruit due to Monilinia fructicola, M. laxa & M. fructigena.Top left-control; top centre-M. laxa; top right-M. fructigena;bottom left-M. fructigena; bottom centre-M. fructicola; bottom right-M.laxa.
Symptoms
Death of young blossoms and associated twigs and leaves; small tan cankers with dark margins on twigs; gummy exudate at base of flowers; brown spore masses on flowers in humid conditions.
Cause
Fungi
Comments
Management
2-3 fungicide applications are required during bloom to control disease; application very important at red bud stage; applications should be made every 14 days or less if there is continued heavy rainfall.
Eutypa dieback
Eutypa lata
Symptoms
Cankers on branches, usually associated with a pruning wound which is several years old; discolored sapwood may extend abovwe and below canker; leaves on branches around canker may suddenly wilt as branch dies; leaves remain attached to branches; discoloured bark and inner wood; gummy amber exudate may be present.
Cause
Fungus
Comments
Management
Infected limbs should be removed 1 ft below any internal symptoms before harvest; if pruning is conducted outwith this time a fungicide should be applied to the pruning wounds.
Jacket rot
Botrytis cinerea
Sclerotinia sclerotiorum
Monilinia laxa
Monilinia fructicola
Symptoms
Brown discoloration of fruit under jacket occurring while flower parts still attached to fruit
Cause
Fungi
Comments
Management
Fungicide treatment applied at full bloom
Powdery midew
Sphaerotheca pannosa
Podosphaera tridactyla

Powdery mildew symptoms on apricot fruit
Symptoms
Round powdery white patches of fungal growth on fruits and leaves; rusty patches on fruits which turn brown and leathery and may crack
Cause
Fungi
Comments
Management
Apply fungicide during bloom and fruit development
Ripe fruit rot
Monilinia fructicola
Monilinia laxa

Symptoms of ripe fruit rot on apricot fruits
Symptoms
Dark brown circular spots on fruit; tan spore masses may be visible in center of spots; diseases fruit may not drop from tree
Cause
Fungi
Comments
Management
A protective fungicide treatment may be necessary if heavy rains are forecast 2-3 weeks prior to harvest
Rust
Tranzschelia discolor
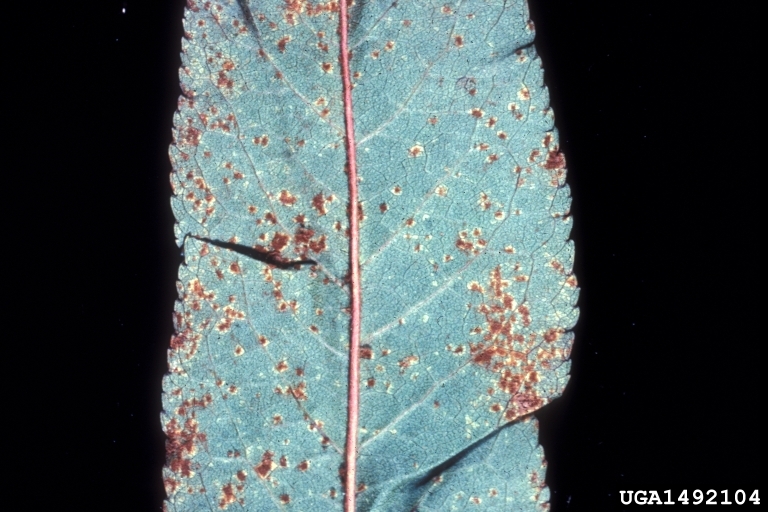
Rust symptoms
Symptoms
Pale yellow-green spots on both upper and lower leaf surfaces which are angular in shape and turn bright yellow in color; spots on lower leaf surface develop orange-red spores.
Cause
Fungus
Comments
Management
Rust can be prevented by spraying trees with protective fungicides; application is usually carried out one, two and three months before harvest in areas prone to early season outbreaks of the disease and after harvest in areas where disease is less problematic or emerges later in the season.
Shot hole disease
Wilsonomyces carpophilus

Shot hole disease symptoms on a peach fruit caused by Wilsonomyces carpophilus. This disease on peach is distinguished by profuse gumming.

Peach fruit displaying symptoms of infection with Shot Hole Disease (Coryneum blight - Wilsonomyces carpophilus).
Symptoms
Brown lesions with purple edge on fruit, twigs and buds; holes in leaves due to lesions which have dried and dropped out; brown lumps developing in the center of lesion (visible with hand lens); buds turning brown or black and exuding sap; tan lesions with brown margins which exude sap on twigs.
Cause
Fungus
Comments
Management
Application of Bordeaux mixture before rains in Fall are sufficient to protect dormant buds and twigs over winter.
Verticillium wilt
Verticillium dahliae
Symptoms
Withering of leaves on one or more spurs on 1 year old wood; leaves are dull and stunted; fruit small; older cherry trees do not recover from disease
Cause
Fungus
Comments
Management
Plant apricot in soil with no history of disease; keep trees adequately fertilized and watered
Category : Bacterial
Bacterial canker
Pseudomonas syringae
Symptoms
Cankers on twigs at bases of flower and leaf buds, in pruning wounds or at the base of spurs which exude amber colored gum; cankers spread upwards and form sunken areas in winter; if pathogen enters dormant buds they may be killed or open normally in Spring before collapsing in early Summer; infected buds may be symptomless.
Cause
Bacterium
Comments
Management
Ensure that a suitable apricot variety and rootstock is chosen based on geographic location and environmental conditions to prevent stress to tree which predisposes tree to canker disease; apply protective copper spray to trees before flowering; prune trees in early summer to decrease likelihood of infection.
Crown gall
Agrobacterium spp

Crown gall
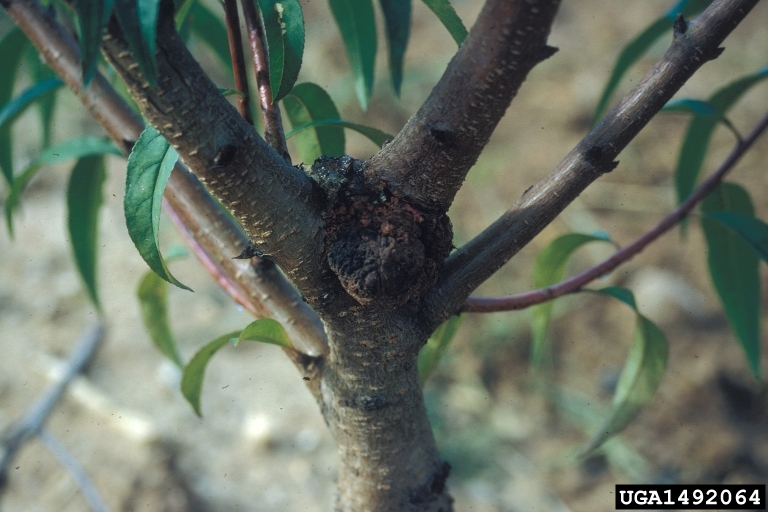

Gall symptom
Symptoms
Galls on root and/or crown of tree which can range in size from so small they are not visible to the naked eye up to 10 cm (4 in) in diameter; galls first become visible as white, fleshy swellings that grow rapidly and become tan to brown in color; galls typically develop at the site of a wound and new galls form adjacent to old ones the next year.
Cause
Bacterium
Comments
Management
Chemical control of the disease is generally ineffective; an effective bacterial biological control is available for commercial production; cultural control methods include: planting only certified, disease-free material, planting apricot in well-draining soil, rotating infected fields with a non-host before apricot is planted and also using good sanitation practices.
Category : Oomycete
Phytophthora root and crown rot
Phytophthora spp.

A tree with a Phytophthora crown rot infection caused by Phytophthora spp. in the field.
Symptoms
Poor new growth; leaves chlorotic, small in size and sparse; fruit may be small, brightly colored and susceptible to sunburn; shoots may suffer from dieback and tree will often die within weeks or months of first signs of infection or decline gradually over several seasons; root crown may show signs of decay which develops into a canker; bark of infected crown tissue turns dark brown; cankers may occur on aerial parts of plant.
Cause
Oomycete
Comments
Management
Plant trees on a small mound to promote drainage; avoid over-watering trees in spring; treat soil around newly planted trees with fungicide; minimize the frequency and duration of water saturated soil; trees should be propagated from resistant rootstock and application of appropriate systemic fungicides may provide some protection from the disease.
Category : Viral
Plum pox virus
Plum pox virus (PPV)
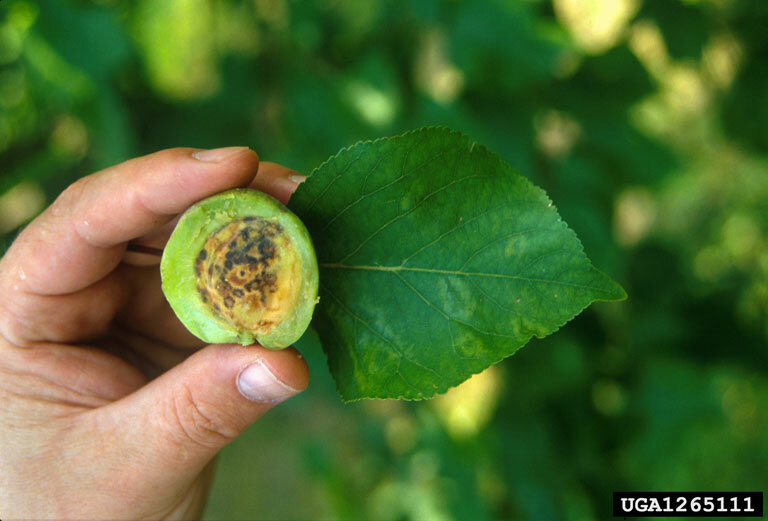

Symptoms of plum pox virus on apricot fruit and leaves.
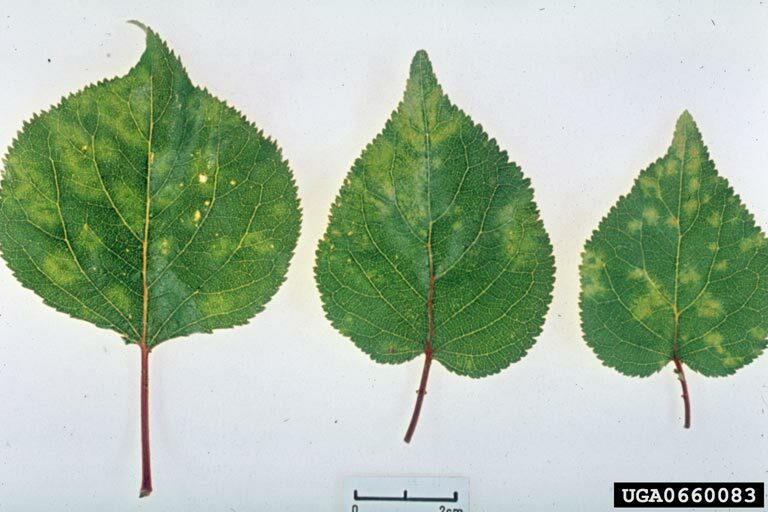

Leaf symptoms of plum pox potyvirus infection on apricot.

Symptoms of plum pox on fruits and seed on apricot, showing brownish depressions and grooves on the surface.

Fruit symptoms of plum pox potyvirus infection on apricot.
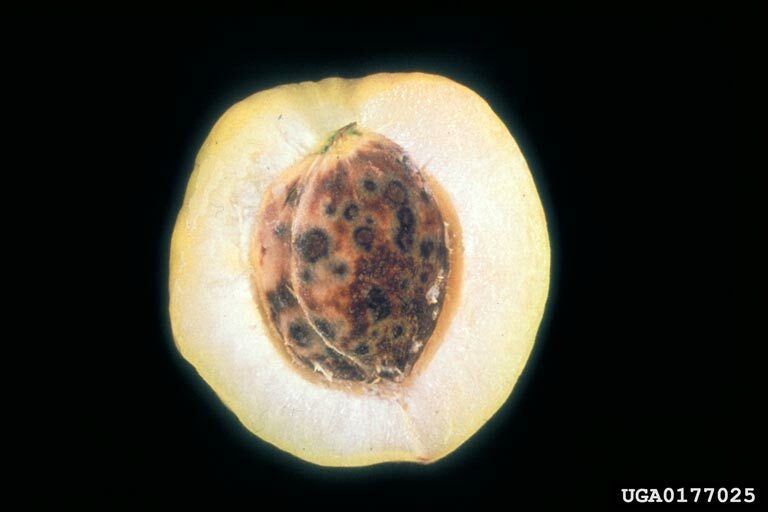
Infected fruit

Symptoms of plum pox virus on apricot fruits
Symptoms
Pale green chlorotic spots, rings and lines on leaves which appear in early summer; pale rings, lines and spots on fruit; fruit flesh dry and flavorless; fruit may be markedly deformed.
Cause
Virus
Comments
Management
Plant certified healthy material; remove infected trees from orchard; chemical sprays to control aphids may prolong spread of virus.




































