Description
Barley, Hordeum vulgare, is an edible annual grass in the family Poaceae grown as a cereal grain crop. It is a tall grass with a hairy stem that stands erect and produces spikelets at the head. Barley is classified under the genus "Hordeum" and the species "vulgare." It's an important cereal crop that belongs to the Poaceae family and is widely cultivated for its various uses in human consumption and industry.
The nodes and internodes make up the stem. The internodes are hollow, as opposed to the solid internodes. The inflorescence, or spike, where the grain is generated, is supported by the stalk.
The heads of the barley seeds are triangular spikes made up of rachis and three spikelets apiece. 20–60 grains are produced by each spike. Barley plants freely tiller and usually have one to six stems. Seed heads are not produced by the tillers. An annual crop, barley may grow to a height of 80 to 100 cm (31.5–39.4 in) and is harvested every year. Barley was initially domesticated in the Fertile Crescent of the Middle East and is sometimes referred to as spring barley or winter barley.
Crop Details
Scientific Name: Hordeum vulgare
Common Name: common barley (En); cebada (Sp); gérste (German); orge (Fr)

Harvested barley grains

Barley beginning to ripen

Barley ready for harvest

Barley ready for harvest

Stubble in harvested field

Green barley field

Green barley

Barley spikes

Barley
Uses & Benefits
Barley is cultivated as a food cereal in the tropics and subtropics in India, Nepal, Tibet, Afghanistan, Russia, Ethiopia, North Africa, and the Andean region of South America. The straw produced is used as animal feed, bedding, and to cover the roofs of houses.In temperate regions, barley is used in malt production to brew beer and make other distilled alcoholic beverages, particularly whisky. Barley flour is a staple grain in North Africa and parts of Asia, used to make unleavened flatbread and porridge.
It is a high-carbohydrate food with moderate amounts of protein, calcium, and phosphorus, as well as small amounts of B vitamins.
Varieties of Barley
There are two main varieties of barley, each with its own characteristics and uses, distinguished by the number of rows of flowers on its flower spike. These varieties include:
Two-row barley: Two-row barley has two types of florets - central florets that produce kernels and lateral florets that don't produce anything. Two-row barley is used more often for malt production because it contains more sugar.
Six-row barley: It has its spike that is notched on opposite sides, with three spikelets at each notch, each containing a small flower that becomes a kernel. Six-row barley is mostly used for animal feed because it has more protein.
Propagation
Basic requirements
Barley is a cool-season crop and thrives in temperate climates. It prefers moderate temperatures during its growth stages. During its growth phases, it prefers warmer temperatures. During the growth season, the ideal temperature ranges for barley cultivation are between 15 and 20 °C (59 and 68 °F). Frost may be tolerated by barley to some extent, but excessive cold or heat could damage the plant's development.
Barley can be grown in a range of soil types, but it prefers well-drained soils with good water-holding capacity. Loamy soils with good organic matter content are generally ideal for barley cultivation. Heavy clay soils can hinder root growth and drainage, while sandy soils may require more frequent irrigation.
Choose a well-drained field with good sunlight exposure and prepare the soil by plowing or tilling to a depth of 6-8 inches. Remove weeds, rocks, and debris from the field. Incorporate organic matter or compost to improve soil structure and fertility.
Growing from Seed
When planting, choose high-quality barley seeds from reputable sources. Select a suitable barley variety based on your region's climate and intended use (e.g., malting, feed, or forage).
Create a smooth and level seedbed to ensure uniform germination and emergence. You can use harrows or other suitable equipment to achieve this. Barley can be sown either by broadcasting or drilling. Drilling is preferred for precise seed placement and even spacing. The recommended seeding rate varies depending on the variety, but a typical range is around 90–120 kg/ha (80–110 lbs/acre).
Plant barley seeds at a depth of about 1-2 inches (2.5–5 cm). Row spacing can vary, but a common recommendation is around 6–8 inches (15–20 cm) between rows.
General Care and Maintenance
Barley requires adequate moisture, especially during its early growth stages. Proper irrigation is important to ensure uniform germination and establishment. However, overwatering should be avoided to prevent waterlogging, which can lead to root diseases. Depending on the local climate and rainfall patterns, barley can be grown as rainfed or irrigated crop. In areas with reliable rainfall, rainfed barley can be successful. In drier regions, irrigation is necessary to supplement water needs. Water stress during critical growth stages, such as flowering and grain filling, can significantly reduce yield. Proper irrigation timing is essential to support these stages.
Mulching can help conserve soil moisture, reduce evaporation, and suppress weed growth. This can be particularly beneficial in areas with limited water availability.
Apply balanced fertilizers based on soil test results and local recommendations. Barley has specific nutrient requirements, especially for nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
Monitor the field for weeds and control them using appropriate methods. Early weed management is crucial to prevent competition with young barley plants. Implement integrated pest management practices to control pests and diseases. Common barley pests include aphids, cutworms, and rust diseases.
Harvesting
Barley is ready to harvest when the stalks and heads have turned from green to yellow and the seed heads are drooping towards the ground. Check the seeds for ripeness before harvest. They should be firm and crunchy and not doughy in texture. Commercially produced wheat is usually harvested using a combine. Smaller plots can be harvested by hand using a scythe or sickle. Small plots can be harvested by snipping off the heads with a pair of scissors.
Please note that specific procedures may vary based on your location, local conditions, and the type of barley you're planting. It's always a good idea to consult with local agricultural experts or extension services for guidance tailored to your region.

Barley being harvested by combine
References
Anderson, P. M., Oelke, E. A. & Simmons, S. R. (2013). Growth and development guide for spring barley. University of Minnesota Extension. Available at: http://www.extension.umn.edu/agriculture/small-grains/growth-and-development/spring-barley/. [Accessed 06 November 14]. Free to access.
CABI Crop Protection Compendium. (2011). Hordeum vulgare datasheet. Available at: http://www.cabi.org/cpc/datasheet/27662. [Accessed 06 November 14]. Paid subscription required.
Mathre, D. E. (Ed.) (1997). Compendium of barley diseases. Available at: http://www.apsnet.org/apsstore/shopapspress/Pages/41809.aspx. Available for purchase from APS Press.
McVay, K., Burrows, M., Jones, C., Wanner, K. & Menalled, F. Montana barley production guide. Montana State University Extension. Available at: http://store.msuextension.org/publications/AgandNaturalResources/EB0186.pdf. [Accessed 06 November 14]. Free to access.
Common Pests and Diseases
Diseases
Category : Bacterial
Bacterial blight (Bacterial leaf blight, Black chaff)
Xanthomonas translucens also known as Xanthomonas campestris
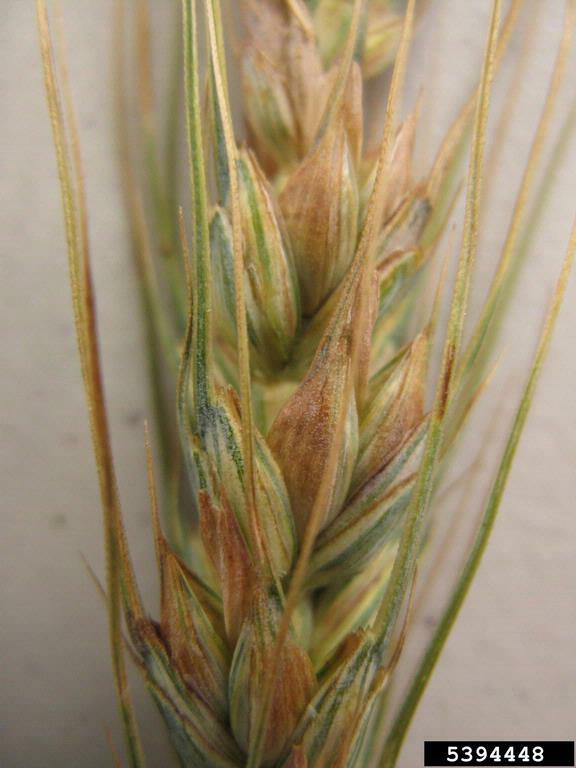

Bacterial blight on wheat glumes
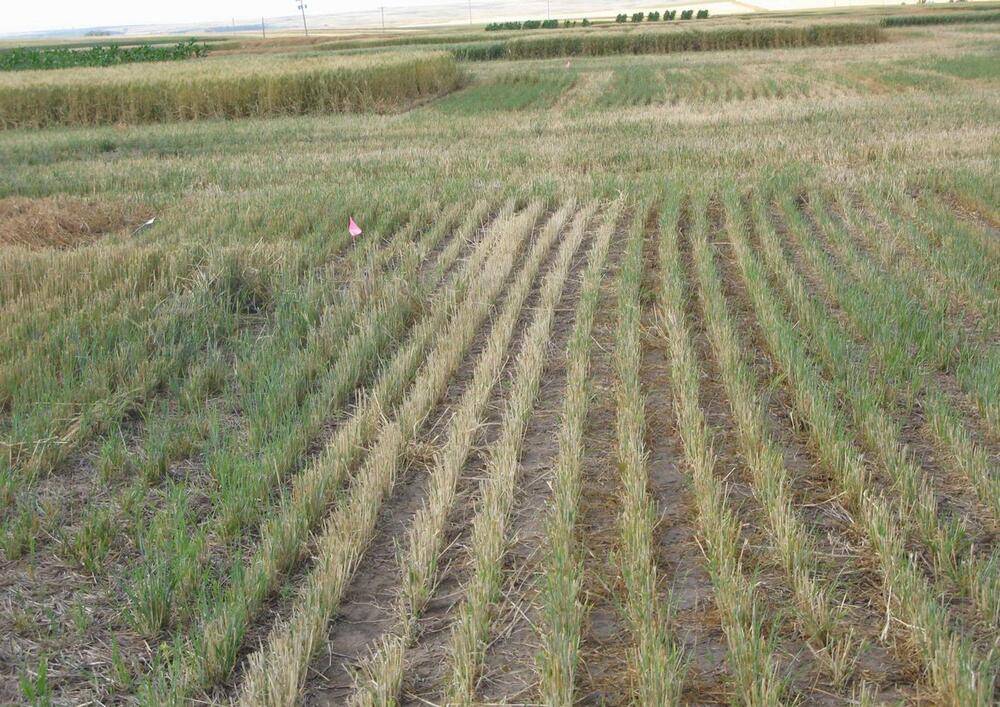

Symptoms in barley field

Leaf lesions generally appear as short necrotic streaks unless they coalesce into larger necrotic areas

Bacterial blight symptoms in chaff row of barley

Bacterial blight symptom
Symptoms
Water soaked spots on foliage; shriveling dead leaves; glossy yellow or brown streaks; plant appears stunted, slow plant growth.
Cause
Bacteria
Comments
Management
Use only certified, disease-free seed; treat seeds with a fungicide prior to planting to prevent diseases which allow bacteria to enter easily; practice crop rotation to reduce disease build-up in soil.
Basal glume rot
Pseudomonas syringae

Wheat spike showing symptoms of basal glume rot (Pseudomonas syringae pv. atrofaciens)
Symptoms
Brown discoloration at base of the glume (bract covering the kernel); dark line where glume attaches to spike; water soaked spots on leaves; yellow and necrotic spots on leaves.
Cause
Bacterium
Comments
Management
Treat seeds with a fungicide prior to planting to prevent diseases which allow bacteria to enter easily; practice crop rotation to reduce disease build-up in soil; plow crop residue into soil.
Category : Viral
Barley stripe
Pyrenophora graminea

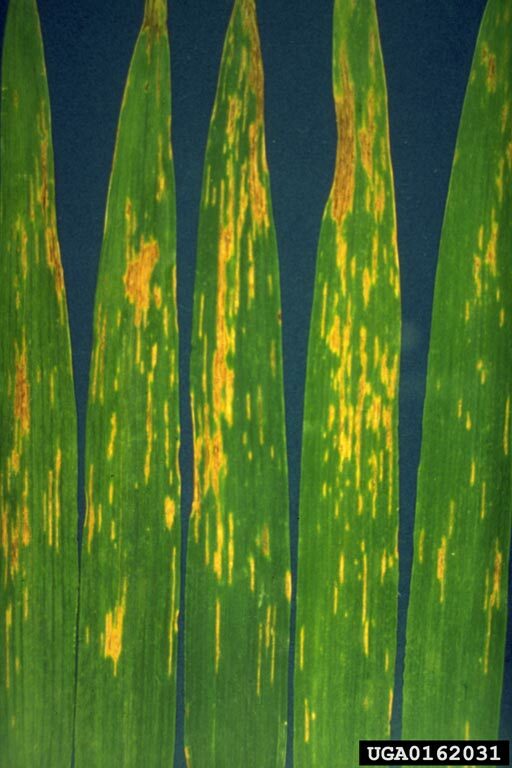
Barley stripe symptoms on barley leaves
Symptoms
Small yellow spots on seedling leaves; yellow to tan stripes along leaf blade before heading; red margins on stripes; death of diseased tissue; heads not emerging; plants stunted.
Cause
Fungus
Comments
Management
Use only certified seed.
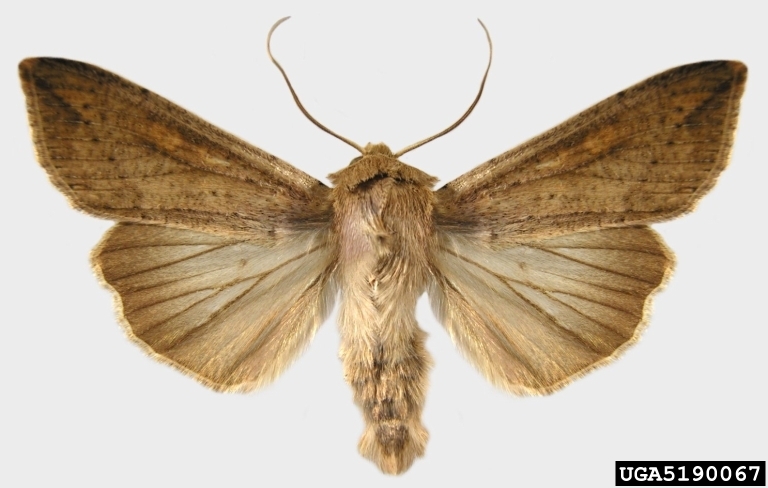
Barley yellow dwarf
Barley yellow dwarf virus (BYDV)

Symptoms of Barley Yellow Dwarf Virus.

Wheat showing an upright posture with thickened, stiff leaves, caused by barley yellow dwarf virus (BYDV). The virus also causes yellowing of the leaves and stunting.

The bright yellow of wheat leaves infected with barley yellow dwarf virus contrasts sharply with the deep green of normal, healthy wheat.
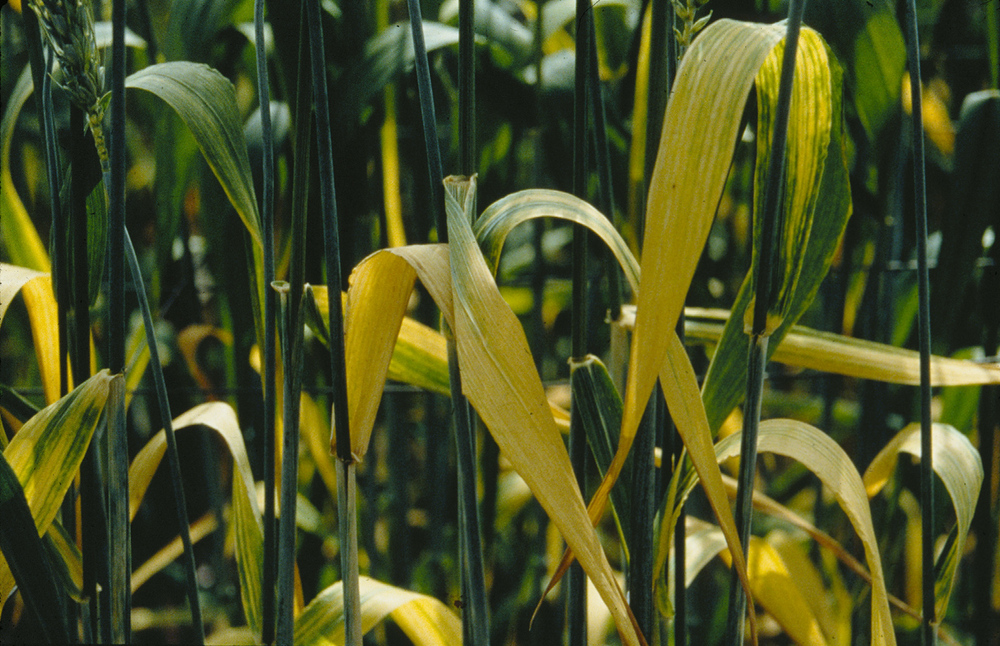

Yellowing of leaves of wheat caused by barley yellow dwarf virus (BYDV).

Barley yellow dwarf virus (BYDV) symptom
Symptoms
Stunted growth of plants; yellow green blotches at leaf tip, leaf margin or leaf blade; leaves turning bright yellow, red or purple.
Cause
Virus
Comments
Management
Grow resistant or tolerant varieties; avoid planting crop very early or very late when aphid populations are high.
Category : Fungal
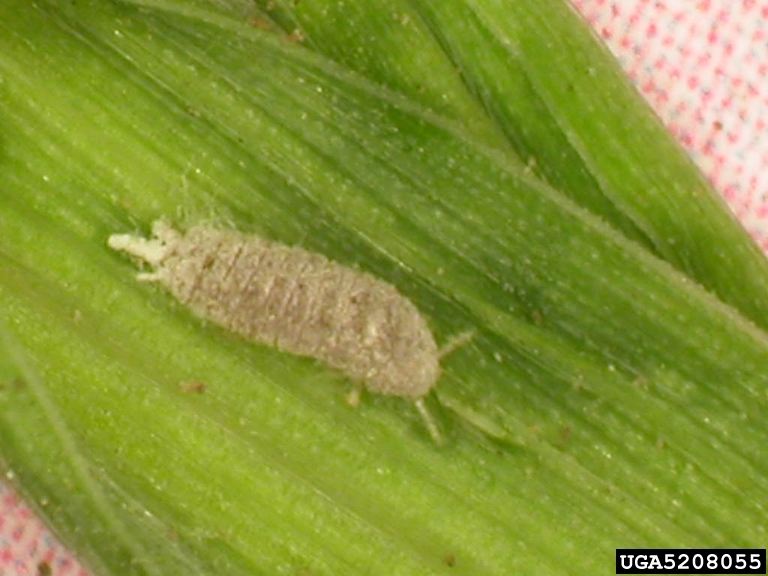
Common root rot
Bipolaris sorokiniana
Cochliobolus sativus
Fusarium culmorum
Fusarium graminearum

Common root rot symptom
Symptoms
Brown lesions on leaves nearest soil extending to stem; resembles drought; death of lower leaves; rotting roots.
Cause
Fungi
Comments
Management
No chemical treatments for this disease; plant crop in late fall to avoid warm soils which favor emergence of disease; do not fertilize crop excessively; use irrigation to reduce water stress.
Covered smut
Ustilago hordei

Covered smut symptoms on barley
Symptoms
Stunted growth; late emergence of heads; kernels replaced with grey fungal masses.
Cause
Fungus
Comments
Management
Use only certified smut-free seed; treat seeds with hot water prior to planting to kill fungi; treat seeds with contact fungicide; grow resistant varieties.
Downy mildew
Sclerophthora rayssiae

Wheat downy mildew symptom- distorted head
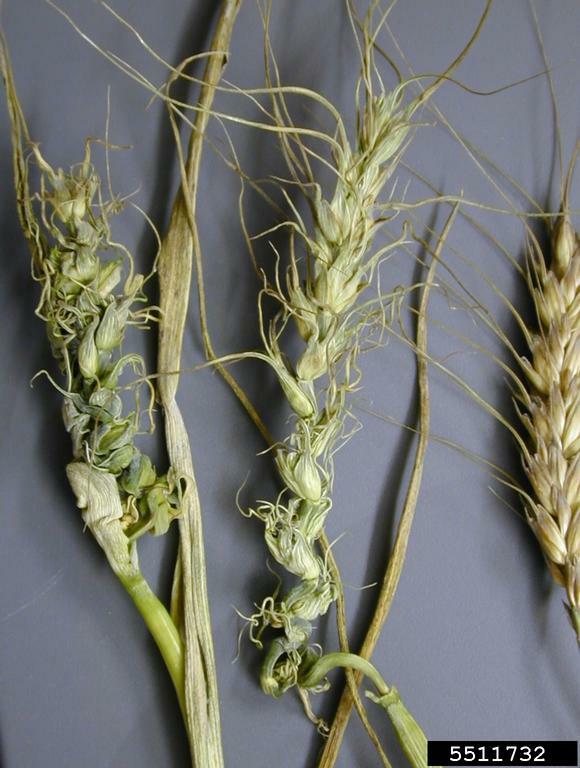

Distortion of wheat heads due downy mildew disease

Distorted wheat heads with crazy top symptoms.
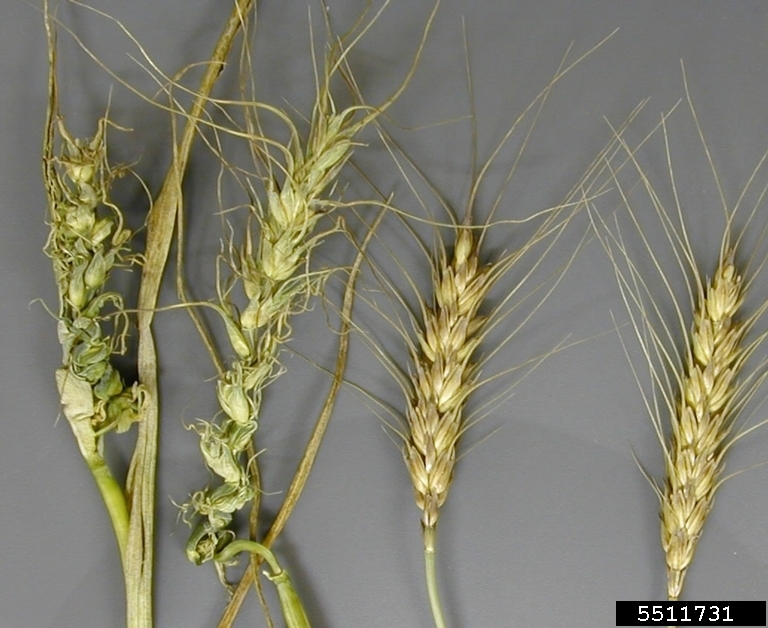

Distortion of wheat heads caused by downy mildew (Sclerophthora macrospora)
Symptoms
Dwarfed and/or deformed plants; flag leaves yellow; leathery leaves; heads distorted; seed not formed.
Cause
Fungus
Comments
Management
Plant crop in well-draining soils; control weeds in field which can act as reservoirs for the disease; sow seed only from disease free plants.
Ergot
Claviceps purpurea

Symptoms

Ergot (Claviceps purpurea) symptoms

Sclerotia bodies

Sclerotia obvious in infected heads
Symptoms
Only head affected; flowers oozing sticky substance (honeydew); head appears dirty due to dust sticking to honeydew; diseased kernels turn to black mass of fungal mycelia.
Cause
Fungus
Comments
Management
Till crop residue deep into soil to prevent spores being released into the air; control weeds, especially grasses, in field which act as a secondary host for disease.
Eyespot (foot rot)
Pseodocercosporella herpotrichoides

Sample wheat plants showing symptoms of foot rot (Pseudocercosporella herpotrichoides).
Symptoms
Eye shaped lesions on basal leaf sheaths and stem; stems shriveled and/or collapsing; plants chlorotic; heads white and undersized.
Cause
Fungus
Comments
Management
Rotate barley with leguminous plants; sow spring barley which is more tolerant of spring frosts.
Fusarium head blight (FHB or scab)
Fusarium graminearum

Fusarium head blight on barley caused by “point” inoculation
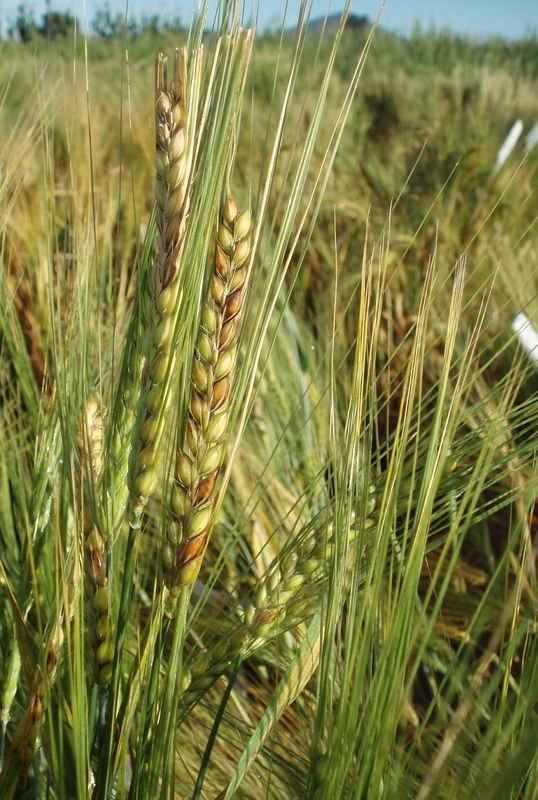

Barley showing symtoms of Fusarium head blight (FHB), with sections of necrosis on the head. Barley normally has more points of initial infection than wheat, i.e., infection starts in multiple places on the head.

Barley spike showing symptoms of Fusarium head blight (FHB): chlorosis, necrosis, and the appearance of black perithecia, fruiting bodies containing spore sacs.

Kernel infected with head blight

Necrosis caused by Fusarium head blight (FHB) on six-row barley.
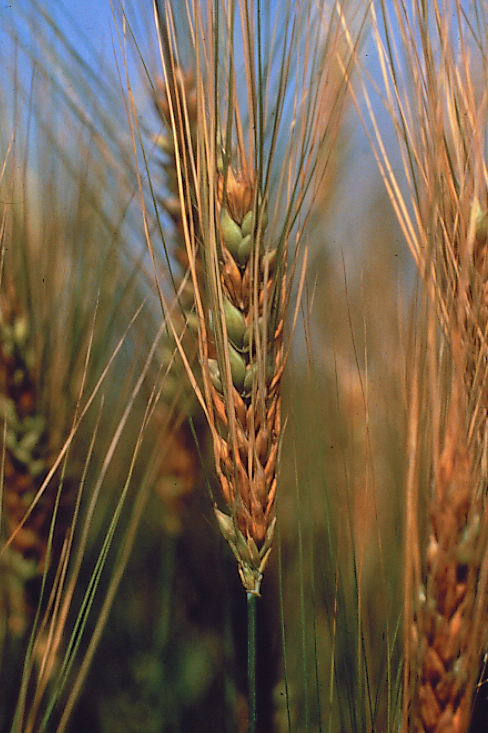

Scab or head blight infected spike
Symptoms
Initial symptoms show bleaching of some of the florets in the spike. Under favorable conditions, premature blight or bleaching of whole spike may occur. As the disease progress head turns tan to brown discoloration. Also, we can see pink or orange color mold appears at the base of the florets. The kernels become shriveled, white, and chalky.
Cause
Fungus
Comments
Management
Grow available resistant varieties. If the disease is severe, spray suitable fungicide.
Loose smut
Ustilago nuda
Ustilago tritici
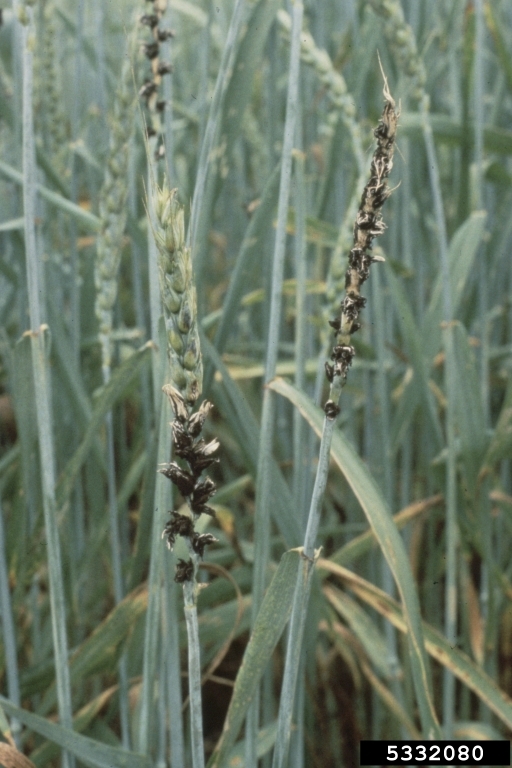

Loose smut infected spikes

Loose smut infected barley spikes

Loose smut symptoms on barley (right) and wheat (left)
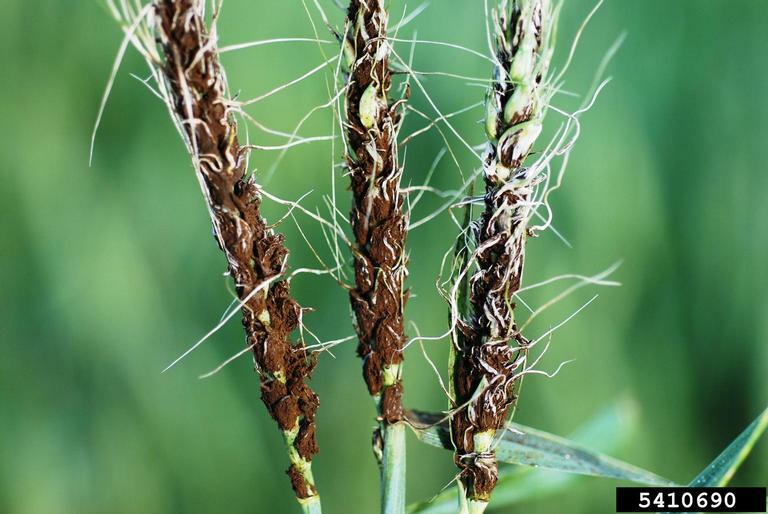

Loose smut symptoms
Loose smut (Ustilago avenae) symptoms
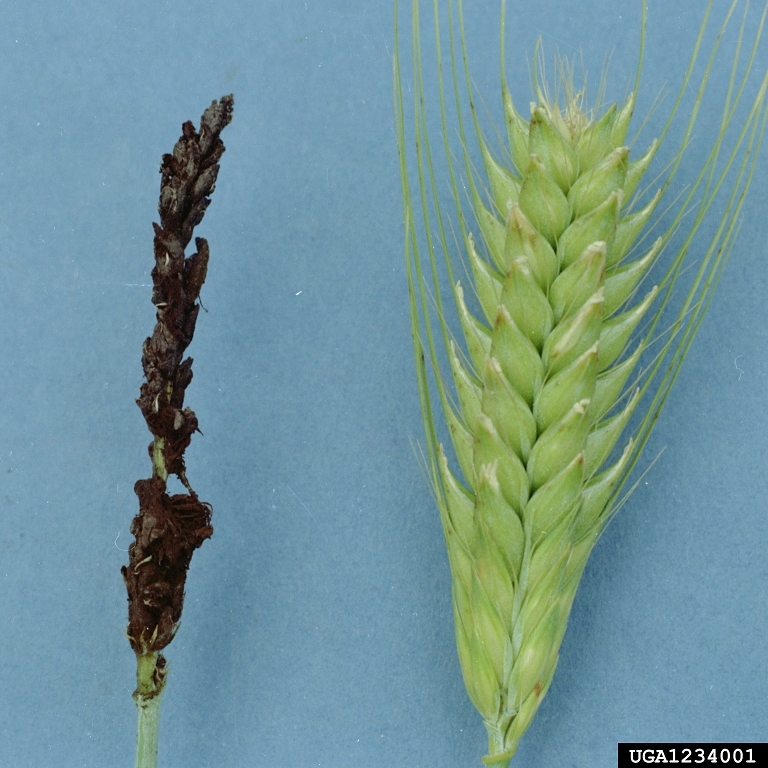

Difference between healthy and loose smut infected barley spike

Loose smut symptoms on barley
Symptoms
Early emergence of heads; dark green or black masses in place of kernels.
Cause
Fungus
Comments
Management
Use only certified smut-free seed; treat seeds with hot water prior to planting to kill fungi; treat seeds with systemic fungicide (fungi inside seed) fungicide; grow resistant varieties.
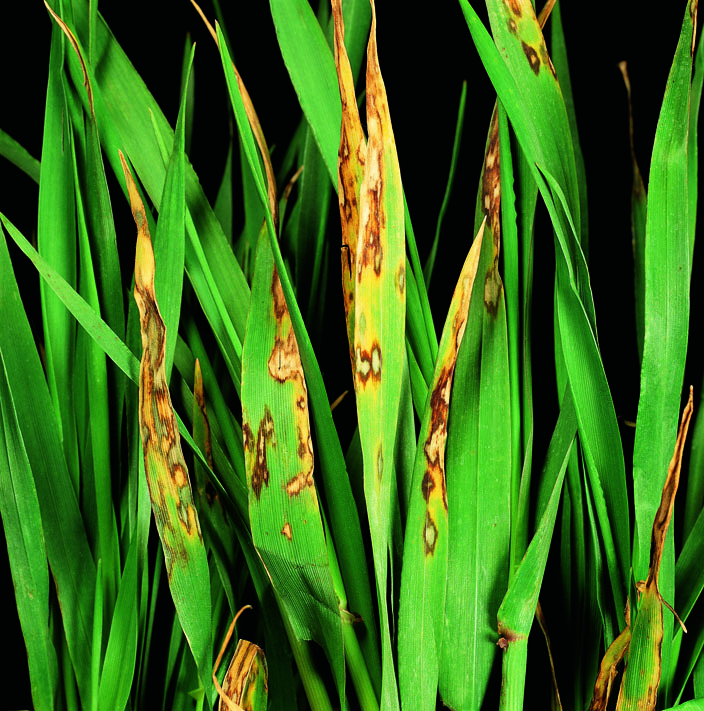
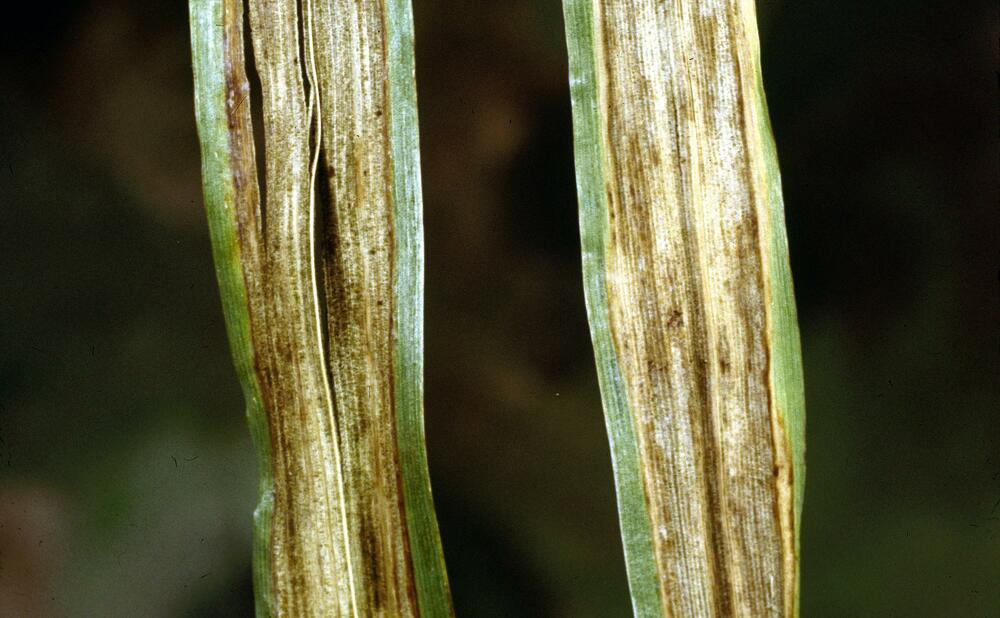
Net blotch
Pyrenophora teres

Close up of a Barley leaf up with Net Blotch.

Net blotch on barley
Symptoms
Dark green water soaked spots; narrow brown blotches with netted appearance, surrounding tissue yellow; stripes running the length of leaf.
Cause
Fungus
Comments
Management
Rotate barley with resistant crops; grow resistant varieties; remove and crop residue from soil surface; destroy volunteer barley plants.
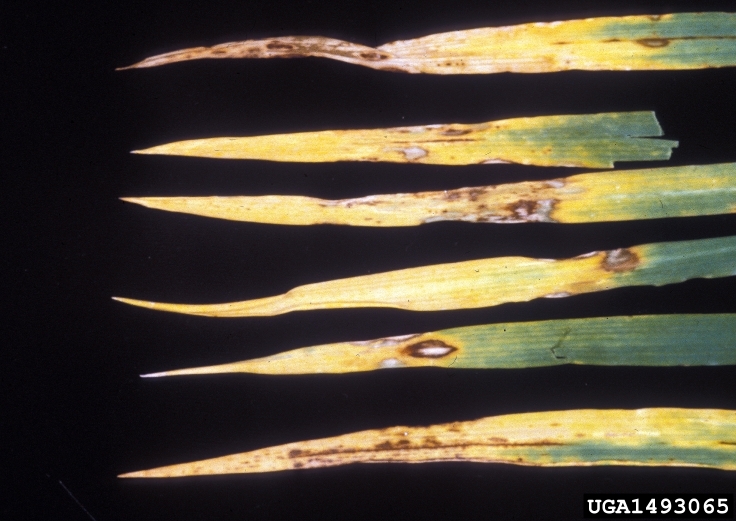
Powder mildew
Blumeria graminis
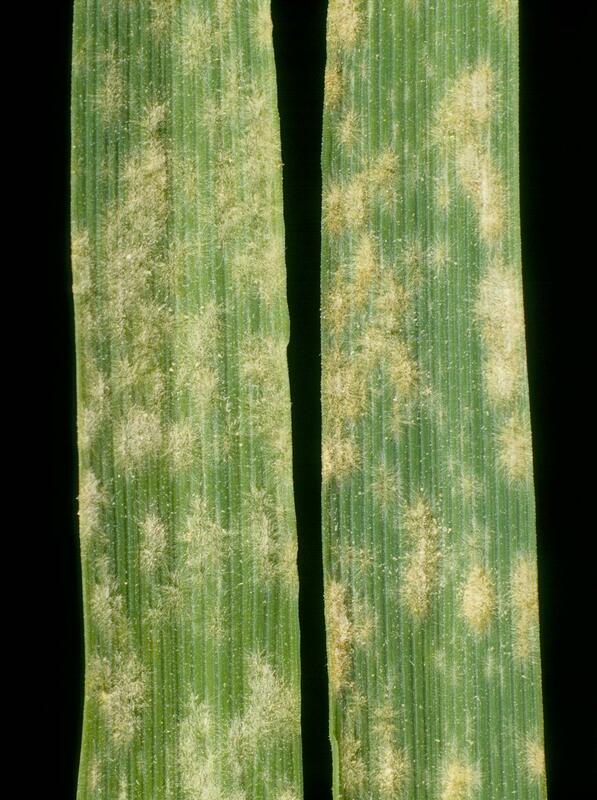

Close up of Barley leaf with Powdery mildew.

Powdery mildew on leaf with cleistothecia present.

Symptoms on lower leaf surface

White cottony patches
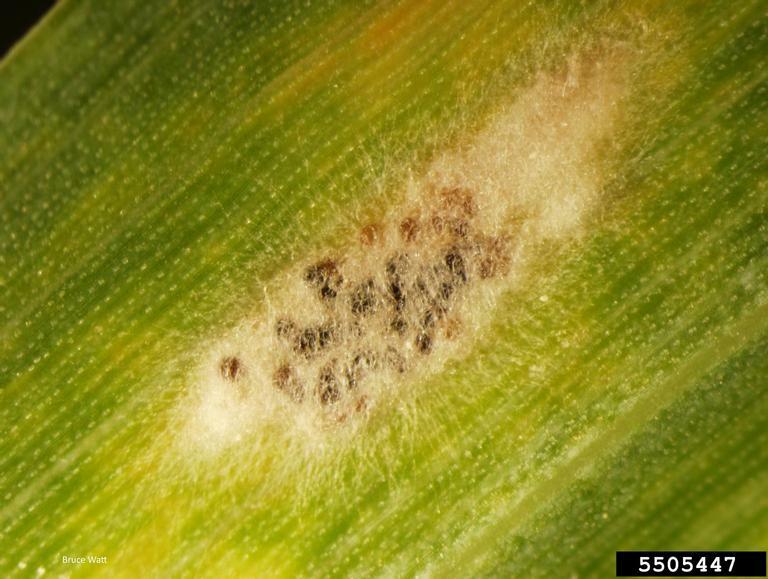
Cleistothecia, of various maturities, developing in dense mycelial mat
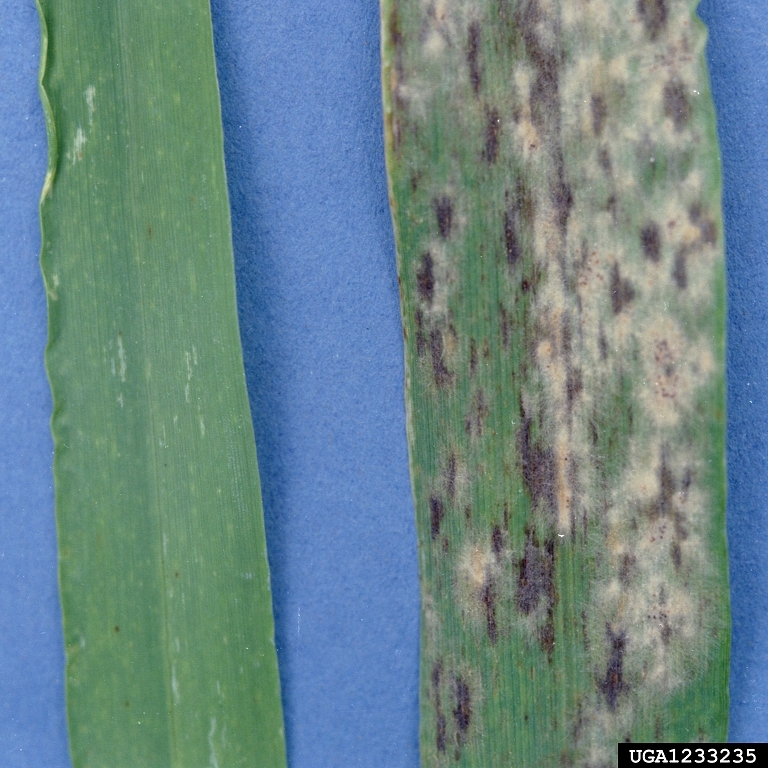

Powdery mildew symptoms on lower and upper surface of barley leaves

Cottony mycelia on leaf.
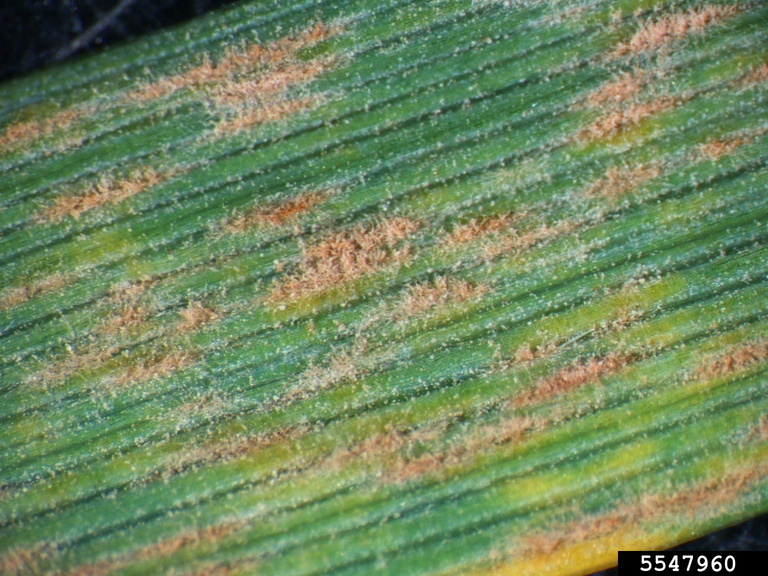

White cottony patches become dull gray- brown color due to development of fruiting bodies (cleistothecia)
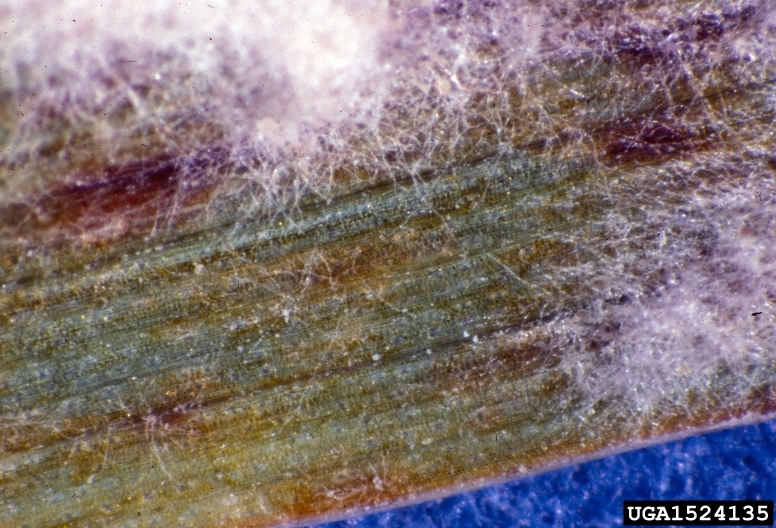

Patches of white cottony growth on lower leaf surface.
Symptoms
Initially the lower leaf surface shows white, cottony patches of fungal growth. The upper surface of these patches exhibit chlorotic spots. As the disease progress, this white cottony patches become dull gray- brown color due to development of fruiting bodies (cleistothecia). The infected plants show slow growth.
Cause
Fungus
Comments
Management
Grow available resistant varieties. Follow crop rotation. Keep the field free from weeds and other unwanted plants. Remove and destroy the infected crop residue.


































































































