Eggplant
Description
Uses
Propagation
References
CABI Crop Protection Compendium. (2010). Solanum melongena datasheet. Available at: http://www.cabi.org/cpc/datasheet/50536. [Accessed 24 November 14]. Paid subscription required. Rowell, B. (2006). Revised. Eggplant. University of Kentucky Cooperative Extension Service. Available at: http://www.uky.edu/Ag/NewCrops/introsheets/eggplant.pdf. [Accessed 24 November 14]. Free to access
Common Pests and Diseases
Diseases
Category : Other
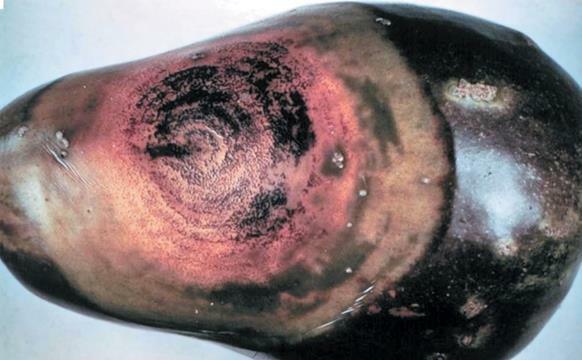
Blossom-end rot n/a
Symptoms
Small water-soaked area on end of fruit where the blossom was occurring on unripe fruit; lesion enlarges and turns sunken, black and leathery in appearance.
Cause
Physiological disorder
Comments
Caused by low calcium concentration in fruit; may result from competition from other competitive ions in soil e.g. potassium, drought stress; fluctuations in soil moisture or application of excessive amounts of nitrogen fertilizer which promotes rapid vegetative growth.
Management
Maintain soil pH at 6.5; lime soil to increase the concentration of calcium in soil and decrease competition with other ions; use mulch to reduce drought stress; avoid ammonium fertilizers as they may increase competition with calcium by increasing ammonium ions in soil, use nitrate instead; avoid over fertilizing.Category : Fungal
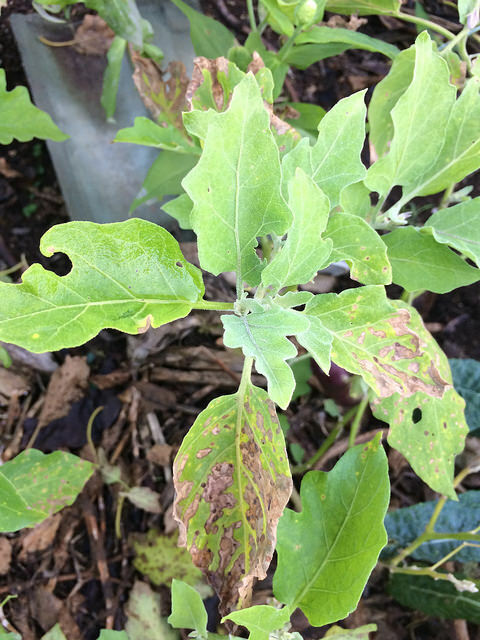
Cercospora leaf spot Cercospora melongenae
Symptoms
Symptoms appear first on lower part of plant and move upwards; initial symptoms are small circular or oval chlorotic spots on leaves which develop light to dark brown centers; as the lesions expand, they may develop concentric zones; severely infested leaves may dry out and curl then drop from the plant.
Cause
Fungus
Comments
Fungus can survive over winter on crop debris in soil.
Management
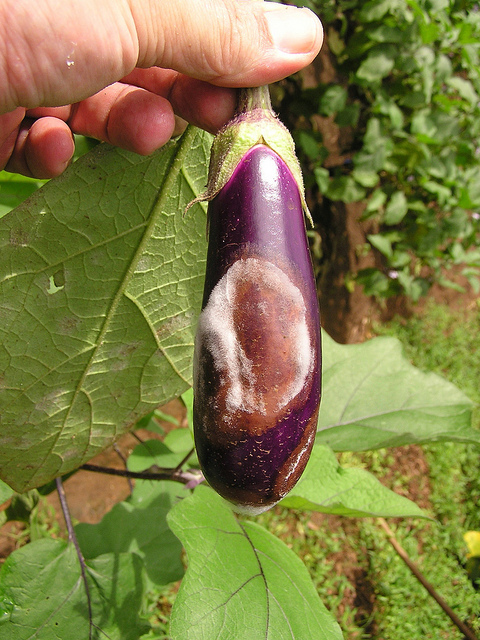
Irrigate plants in the morning to allow plenty time for plants to dry out during the day; irrigate at base of plant to avoid leaf wetness; use adequate plant spacings to decrease humidity in the plant canopy; applications of appropriate protective fungicides can protect plants from disease.Colletotrichum fruit rot Colletotrichum melongenae
Symptoms
Sunken lesions on the fruit filled with pinkish fungal ooze; severely infected plants drop to the ground with the pedicel still attached.
Cause
Fungus
Comments
Disease favors warm, wet conditions; exacerbated by overhead irrigation.
Management
Avoid sprinkler irrigation when fruit is ripening; rotate crops with other non-solanaceous plants; applications of appropriate protective fungicides may be required if disease is in the area.
Damping-off
Fusarium
Pythium spp.
Rhizoctonia spp.
Symptoms
Failure of seedling to emerge; light brown, seedlings with light brown to redwater-soaked roots and stems; collapse of plants; plant dry up and die; stunted plant growth; rotting taproot with few lateral roots
Cause
Fungi
Comments
Disease favors warm weather and very wet soil with poor drainage
Management
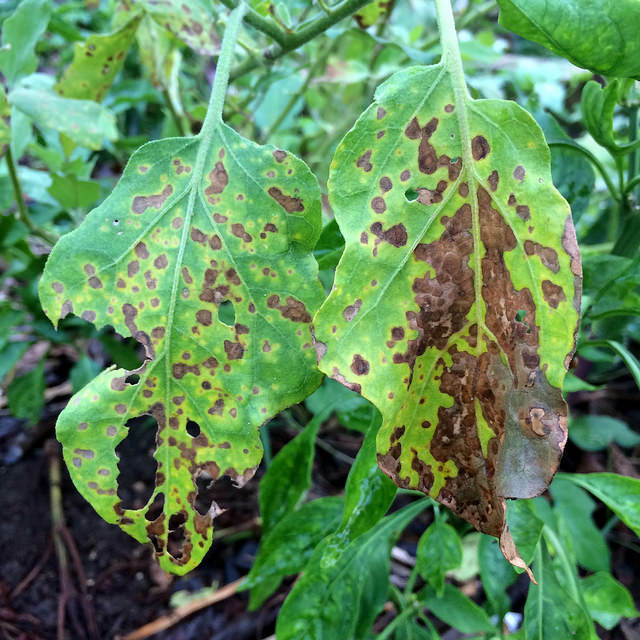
Plant pathogen-free seed or transplants that have been produced in sterilized soil; apply fungicide to seed to kill off any fungi; shallow plant seeds or delay planting until soil warmsEarly blight Alternaria tomatophilia
Symptoms
Premature dropping of lower leaves; brown-black spots on leaves; spots covering leaf surface; alternating rings of light and dark on leaves; yellowing dry leaves; large sunken area of concentric rings and black velvety texture at stem end of fruit
Cause
Fungus
Comments
Disease can spread rapidly after plants have set fruit
Management
Apply fungicide at first sign of disease; destroy any volunteer solanaceous plants (tomato, potato, nightshade etc); practice crop rotationPhomopsis fruit rot Phomopsis vexans
Symptoms
Circular brown spots with lighter centers on fruits; infested leaves may turn yellow and drop from plant; dark cankers may form on stems; symptoms on fruit begin as pale sunken areas which are oval in shape, these area grow bigger and become depressed; lesions may coalesce to cover all or most of the fruit
Cause
Fungus
Comments
Fungus survives in crop debris in the soil; emergence of the disease if favored by hot, humid weather conditions; fungus spreads primarily by splashing water
Management
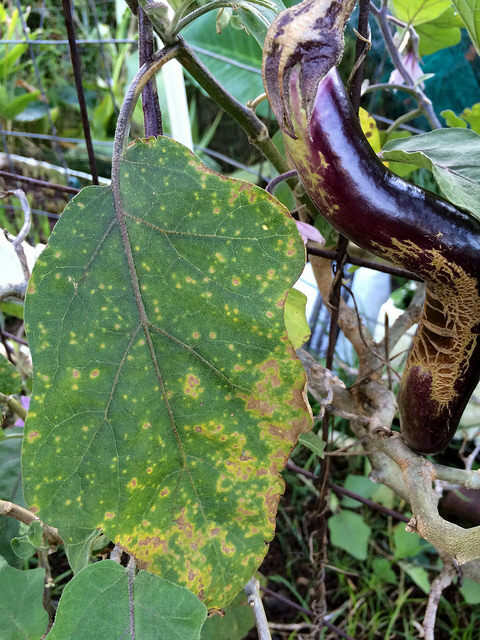
Destroy infected plant material to reduce levels of inoculum; plant only disease free seed and clean transplants; applications of appropriate fungicides may be required to control the diseasePowdery mildew Leveillula taurica
Symptoms
White, powdery spots on leaves, shoots, flowers and fruit; yellow, twisted leaves; leaves dropping
Cause
Fungus
Comments
Disease favors shady conditions and poor air circulation
Management
Avoid stressing plants by providing them with adequate irrigation and fertilizer; use adequate spacings when planting to avoid overcrowdingVerticillium wilt Verticillium spp.
Symptoms
Symptoms appear first on lower leaves and spread upwards; symptoms include yellow blotches on lower leaves, rapid yellowing and the edges of leaves rolling inward; leaves on severely infested rats turn brown and dry
Cause
Fungus
Comments
Can survive in soil indefinitely; disease has a broad host range; emergence is favored by cool temperatures
Management
Plant resistant varieties; sanitize all equipment on a regular basis; rotate with non-susceptible crops; fumigation of soil can reduce levels of inoculum; solarizing soil is also effective but must be done in the middle of summer when the eggplants are usually grownCategory : Oomycete
Phytophthora blight Phytophthora capsici
Symptoms
Wilting plants; plant death; water soaked root; few secondary roots; brown discoloration on roots; water-soaked brown lesions on stem at soil line
Cause
Oomycete
Comments
Disease emergence is favored by water saturated soils; disease is commonly spread by infected transplants and contaminated water
Management
Rotate crops away from susceptible plants for a period of 2 years if disease id present; avoid excessive overhead irrigation; only plant in well-draining soilsPests
Category : Insects
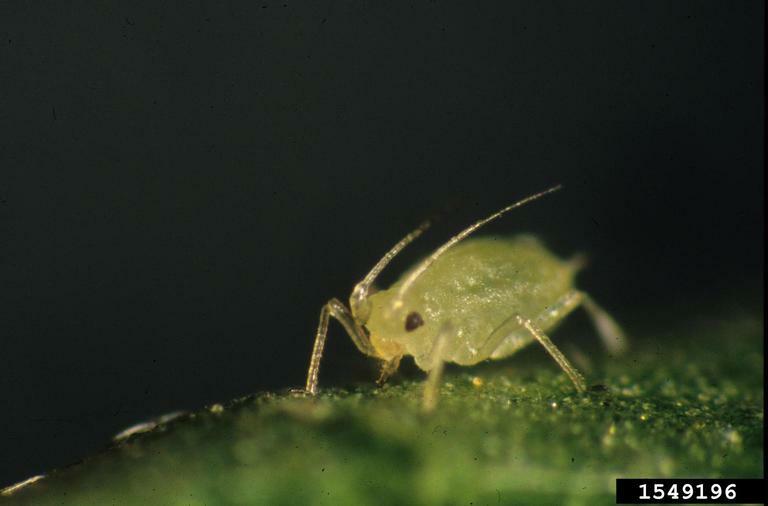
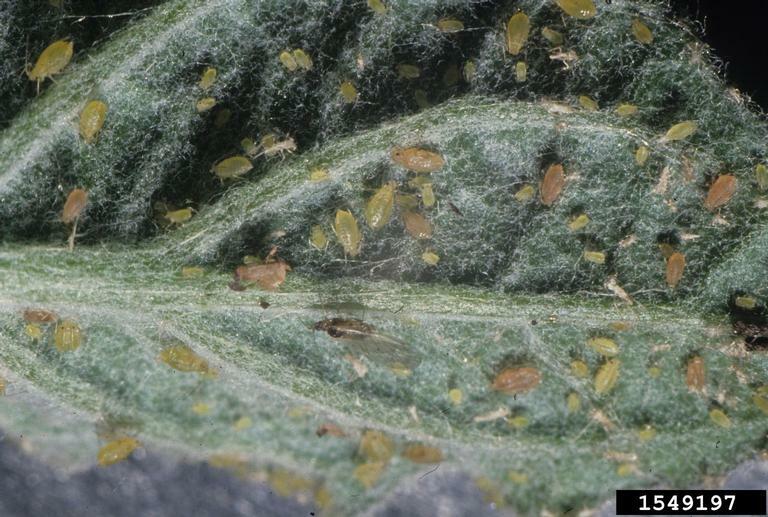
Aphids (Peach aphid, Potato aphid)
Myzus persicae
Macrosiphon euphorbiae
Symptoms
Small soft bodied insects on underside of leaves and/or stems of plant; usually green or yellow in color, but may be pink, brown, red or black depending on species and host plant; if aphid infestation is heavy it may cause leaves to yellow and/or be distorted, necrotic spots on leaves and/or stunted shoots; aphids secrete a sticky, sugary substance called honeydew which encourages the growth of sooty mold on the plants.
Cause
Insect
Comments
Distinguishing features of aphids include the presence of cornicles (tubular structures) which project backwards from the insect's body; aphids will generally not move very quickly when disturbed; aphids may also transmit plant viruses to the plant when they feed.
Management
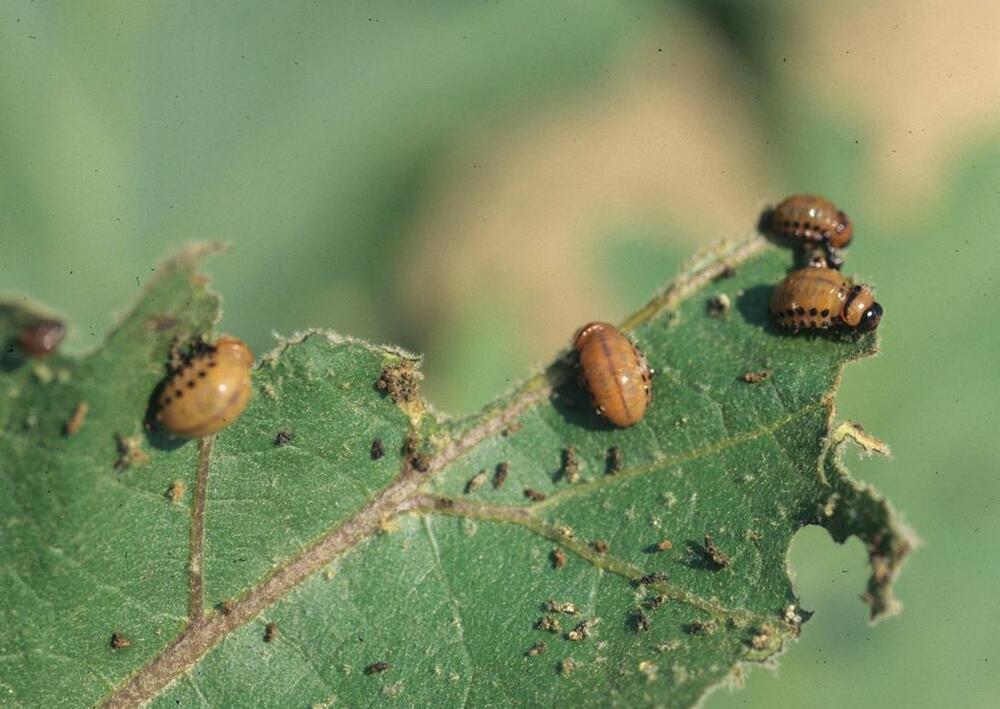
If aphid population is limited to just a few leaves or shoots then the infestation can be pruned out to provide control; check transplants for aphids before planting; use tolerant varieties if available; reflective mulches such as silver colored plastic can deter aphids from feeding on plants; sturdy plants can be sprayed with a strong jet of water to knock aphids from leaves; insecticides are generally only required to treat aphids if the infestation is very high - plants generally tolerate low and medium level infestation; insecticidal soaps or oils such as neem or canola oil are usually the best method of control; always check the labels of the products for specific usage guidelines prior to use.Colorado potato beetle Leptinotarsa decemlineata
Symptoms
Feeding damage to foliage; if infestation is severe or if left untreated plants can be completely defoliated; adult insect is a black and yellow striped beetle; larvae are bright red with black heads when they first hatch and change color to pink; larvae have two rows of black spots.
Cause
Insect
Comments
Adult beetles emerge in spring; female beetles lay eggs in batches of up to two dozen; eggs are orange-yellow and are laid on undersides of leaves; a female can lay 500 or more eggs over a four to five week period.
Management
Control of Colorado potato beetle can be challenging as they have developed high levels of insecticide resistance; in the home garden planting early maturing varieties of potato allows the plants to escape from most damage; adults and larvae should be hand picked from plants and destroyed in soapy water; applications of Bacillus thuringiensis can be effective at controlling larvae but should be applied frequently; some insecticides, including spinosad, are still effective against adult beetles.
Cutworms
Various species including:
Agrotis spp.
Peridroma saucia
Nephelodes minians
etc.
Symptoms
Stems of young transplants or seedlings may be severed at soil line; if infection occurs later, irregular holes are eaten into the surface of fruits; larvae causing the damage are usually active at night and hide during the day in the soil at the base of the plants or in plant debris of toppled plant; larvae are 2.5–5.0 cm (1–2 in) in length; larvae may exhibit a variety of patterns and coloration but are usually dirty gray or brown to black with dark spots or lines and will curl up into a characteristic C-shape when disturbed
Cause
Insect
Comments
Cutworms have a wide host range and attack vegetables including asparagus, bean, cabbage and other crucifers, carrot, celery, corn, lettuce, pea, pepper, potato and tomato
Management
Remove all plant residue from soil after harvest or at least two weeks before planting, this is especially important if the previous crop was another host such as alfalfa, beans or a leguminous cover crop; plastic or foil collars fitted around plant stems to cover the bottom 3 inches above the soil line and extending a couple of inches into the soil can prevent larvae severing plants; hand-pick larvae after dark; spread diatomaceous earth around the base of the plants (this creates a sharp barrier that will cut the insects if they try and crawl over it); apply appropriate insecticides to infested areas of garden or field if not growing organically
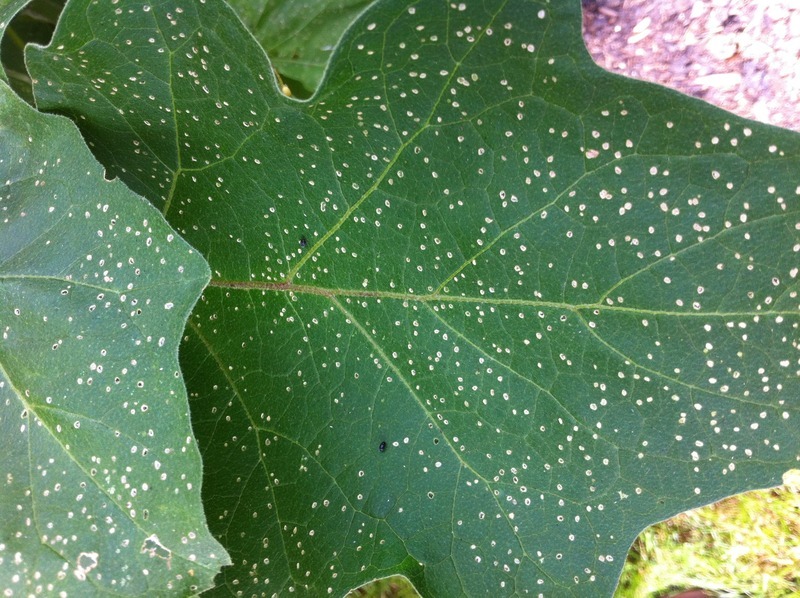
Flea beetles
Epitrix fuscula
Epitrix hirtipennis
Symptoms
Small holes or pits in leaves that give the foliage a characteristic “shothole” appearance; young plants and seedlings are particularly susceptible; plant growth may be reduced; if damage is severe the plant may be killed; feeding damage may also occur on the fruit; the pest responsible for the damage is a small (1.5–3.0 mm) dark colored beetle which jumps when disturbed; the beetles are often shiny in appearance
Cause
Insect
Comments
Flea beetles may overwinter on nearby weed species, in plant debris or in the soil; insects may go through a second or third generation in one year
Management
In areas where flea beetles are a problem, floating row covers may have to be used prior to the emergence of the beetles to provide a physical barrier to protect young plants; plant seeds early to allow establishment before the beetles become a problem - mature plants are less susceptible to damage; trap crops may provide a measure of control - cruciferous plants are best; application of a thick layer of mulch may help prevent beetles reaching surface; application on diamotecoeus earth or oils such as neem oil are effective control methods for organic growers; application of insecticides containing carbaryl, spinosad, bifenthrin and permethrin can provide adequate control of beetles for up to a week but will need reapplied
Hornworms (Tomato hornworm, Tobacco hornworm)
Manduca quinquemaculata
Manduca sexta
Symptoms
Feeding damage to leaves or leaves stripped from plant; heavy infestation may result in damage to fruit appearing as large open scars; large green caterpillars may be spotted on plant; caterpillars may reach in excess of 7.5 cm (3 in) in length and possess a spike at the end of their body; most common species have 7 diagonal stripes on sides or 8 v-shaped markings on each side; single eggs may be present on leaves and measure approx 1.3 mm in diameter; eggs are in initially light green in color and turn white prior to hatching
Cause
Insect
Comments
Insect overwinters as pupa in soil; typically undergoes 2 generations per year; heavy infestations are more common in warm areas
Management
Hand pick larvae from plants leaving any parasitized larvae behind to promote populations of natural enemies (these larvae can be distinguished by the presence of white, oblong-shaped cocoons on their backs); sprays of Bacillus thuringiensis are organically acceptable and highly effectiveStinkbugs (Various) Various
Symptoms
Dark colored pinpricks on fruit surrounded by a lighter area that turns yellow or remains light green; stink bugs often carry pathogens in their mouthparts which can cause secondary infections and decay of fruit; adult insect is shield-shaped and brown or green in color; may have pink, red or yellow markings; eggs are drum shaped and laid in clusters on the leaves; larvae resemble the adults but are smaller
Cause
Insect
Comments
Several types of stink bug can cause damage to tomatoes; adult insects overwinter under leaves, on legumes, blackberries or on certain weeds such as mustard or Russian thistle
Management
Remove weeds around crop which may act as overwintering sites for stink bugs and practice good weed management throughout the year; organically accepted control methods include the use of insecticidal soaps, kaolin clay and preservation of natural enemies; chemical treatments are not recommended for tomatoes that are to be processed for paste or canning unless secondary infections with other pathogens are a concernCategory : Mites
Mites (Carmine mite, Two-spotted spider mite)
Tetranychus cinnabarinus
Tetranychus urticae
Symptoms
Leaves stippled with yellow; leaves may appear bronzed; webbing covering leaves; mites may be visible as tiny moving dots on the webs or underside of leaves, best viewed using a hand lens; usually not spotted until there are visible symptoms on the plant; leaves turn yellow and may drop from plant
Cause
Arachnid
Comments
Spider mites thrive in dusty conditions; water-stressed plants are more susceptible to attack